PostgreSQL

Introduction
On this occasion, I think it is very important to share a series of tutorials about the administrator of the PostgreSQL database. Because in my opinion it is one of the best database administrators in relation to relational DB. In this first part of the tutorial, I would like to focus more than anything on the first steps to start with this important tool. Teaching the installation and some features that will help people get started. As I go through the whole series, I will teach more complex functionalities that will help with the real development of a project. I hope you like it.
What Will I Learn?
- Understanding PostgreSQL.
- Instalation PostgreSQL 9.6 (Debian Jessie 8).
- Creation of users.
- Creation of database.
- You will learn : Create, Delete Table.
- You will learn : Insert, Update, Select, Remove register.
- Grant privileges to the user created.
Difficulty
- Basic
Understanding PostgreSQL.
PostgreSQL is a relational database manager, PostgreSQL's source code is available under a liberal open source license, is considered one of the most advanced database managers today; the first version of the code was public on August 1, 1996, released under the PostgreSQL License and developed by PGDG "PostgreSQL Global Development Group". Now are in your version 10.3 but for this tutorial we will used the version 9.6, It has support for different OS like:
- BSD
- macOS
- Linux
- Solaris
- Windows
In this opportunity we will use the operating system: Debian Jessie 8.
Installation PostgreSQL 9.6 (Debian Jessie 8).
- First you have to import repository signing key, and update the package lists, with the following command:
wget --quiet -O - https://www.postgresql.org/media/keys/ACCC4CF8.asc | sudo apt-key add -
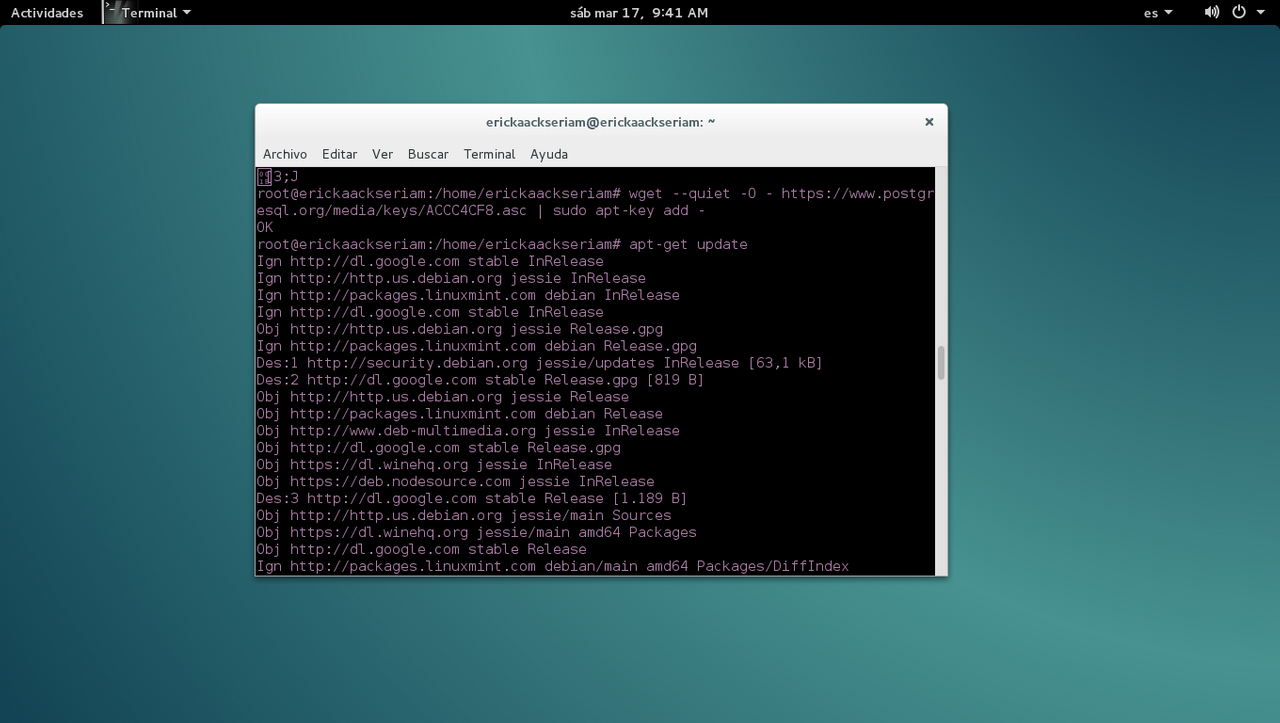
- Second, as sudo (superuser) , you can update with
sudo apt-get update
- Third, you can to install as sudo:
sudo apt-get install postgresql-9.6
Creation of users.
Before of to create users, if you want change the default password of the user Postgres:
You can use the following command as root:
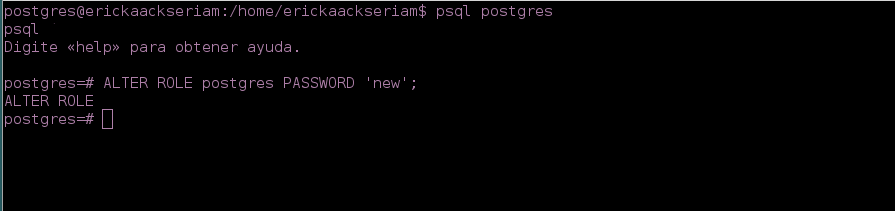
# su postgresand afterpsql postgresAfter, you can to change the password with:
postgres=# ALTER ROLE postgres PASSWORD 'new';
To create the user, you can make the following:
- You must create the user as root:
#su postgres
createuser -D -S -R -l new_user

- After, you can connect with the server PostgreSQL to enter the password of created user:
psql postgres
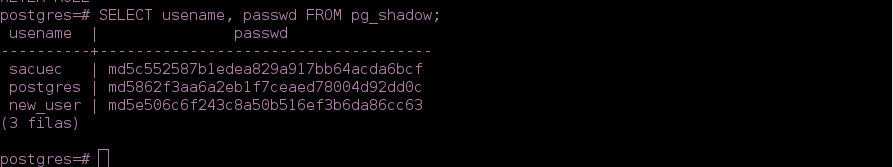
- We check the user created:
postgres=# SELECT usename, passwd FROM pg_shadow;
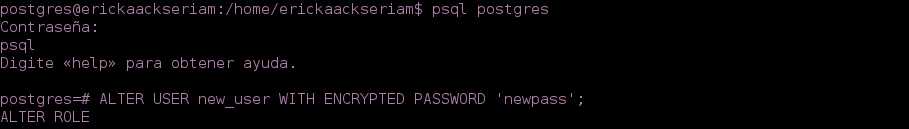
- After of the connection , you can assign the password:
postgres=# ALTER USER new_user WITH ENCRYPTED PASSWORD 'newpass';
Creation of database
- You must create database as root:
#su postgres
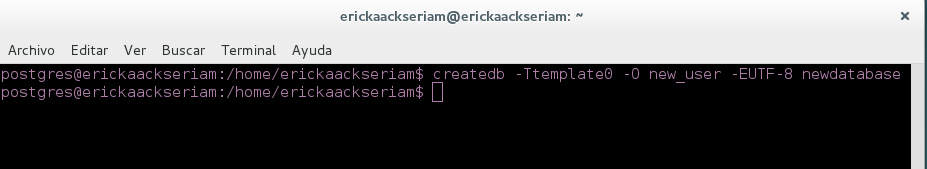
- After, you can create the database (first, enter the template of the database "template0", you can assign the user created previously in this case is "new_user", the coding of the database "UTF-8" and after the name of the database) :
createdb -Ttemplate0 -O new_user -EUTF-8 newdatabase
- After, you can connect with the server PostgreSQL to check the changes
postgres@erickaackseriam:~$ psql postgres
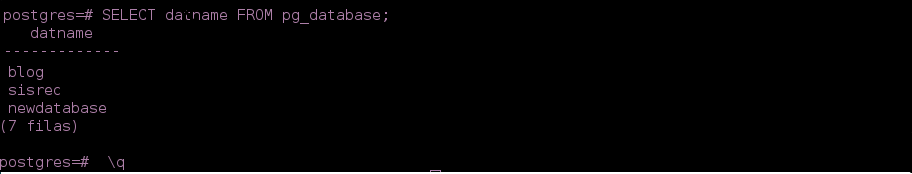
- We check the changes
postgres=# SELECT datname FROM pg_database;
- Then to exit the connection:
postgres=# \q
Create Table to database
For example, we will to make a table with the name "user":
- First, you must enter as root:
#su postgres
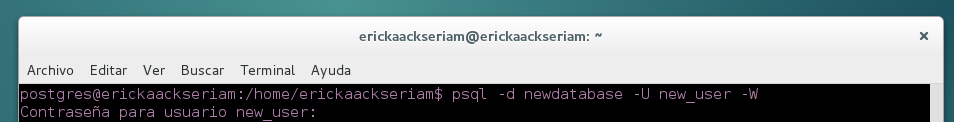
- After, you can connect with the server PostgreSQL and Choose the database
psql -d newdatabase -U new_user -W
- Then, you can create the table with the following command
CREATE TABLE person (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
name varchar(30) NOT NULL,
password varchar(30) NOT NULL,
email varchar(30) NOT NULL);
In this case the table will have the name "user", in the parentheses are the columns of the table, then you enter the datatype (varchar, int). In this case:
Id:
Has the datatype SERIAL as primary key and NOT NULL.br>name:
Has the datatype varchar with a length of 30.password:
Has the datatype varchar with a length of 30.email:
Has the datatype varchar with a length of 30.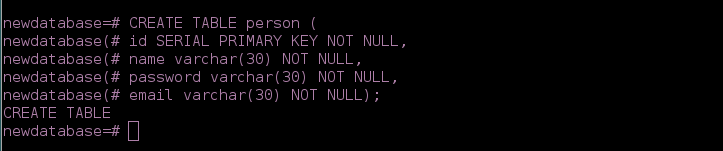
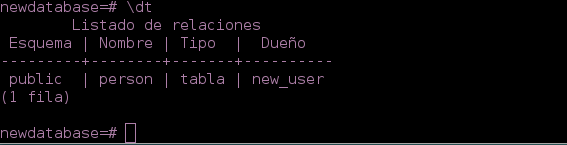
- To show the table created
\dt
Delete Table
- First, you must enter as root:
#su postgres
- After, you can connect with the server PostgreSQL and Choose the database
psql -d newdatabase -U new_user -W
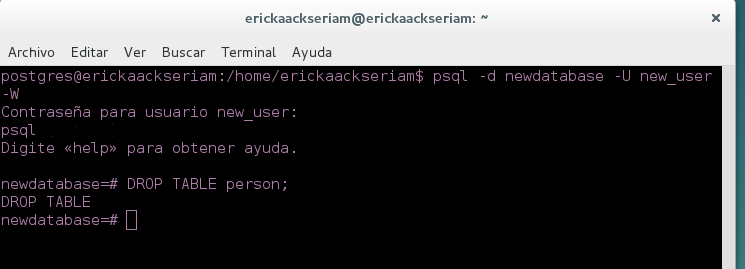
- Then, remove the table with the following command
DROP TABLE person;
Inserting data to the table
- First, we enter as root:
#su postgres
- After, you can connect with the server PostgreSQL and Choose the database
psql -d newdatabase -U new_user -W
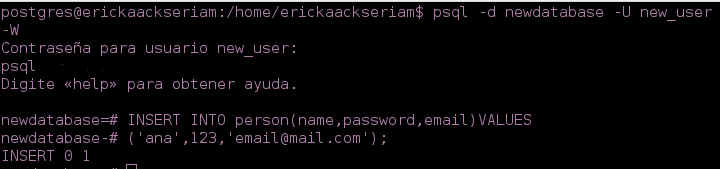
- You can execute the registration with INSERT INTO. With this operation, you can insert a single row .
INSERT INTO person (name, password,email)
VALUES ('ana', '123','[email protected]');
Updating Data in the table
- First, we enter as root:
#su postgres
- After, you can connect with the server PostgreSQL and Choose the database
psql -d newdatabase -U new_user -W
- UPDATE with
UPDATE person SET password='updatepass'
where email='[email protected]';
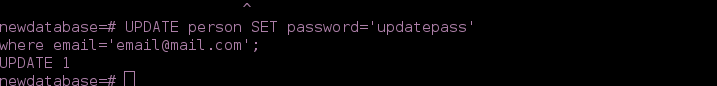
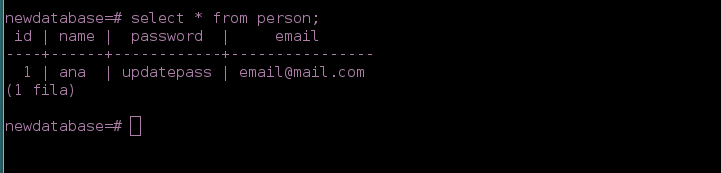
-We check the changes with
SELECT * FROM person;
Delete Data of the table
You can use this SQL to remove the data in the table:
(Where email is "email@mail.com")
DELETE FROM person where email='[email protected]';
Grant privileges to the user created.
- You can proceed to grant privileges to the table created with:
(For example for all the privileges of the table)
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE newdatabase TO new_user;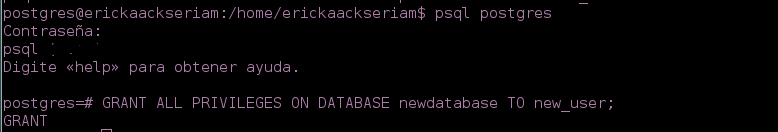
Posted on Utopian.io - Rewarding Open Source Contributors